A highly invasive pest is quietly spreading through Queensland’s waterways, with experts sounding the alarm over its devastating potential.
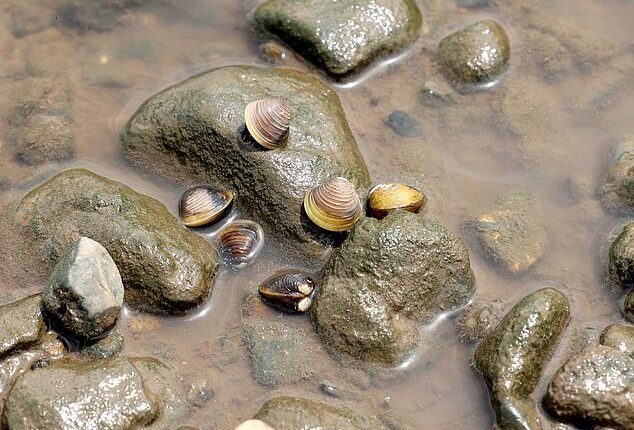
The freshwater gold clam – a species first recorded in Australia in February 2024 – has now been detected in multiple locations across Brisbane’s river systems, sparking concern for native wildlife and water quality.
Biosecurity Queensland issued a warning recently after the tiny but destructive shellfish was spotted in Kedron Brook by a dog walker.
‘Freshwater gold clam is a small shellfish, with a big threat on our freshwater ecosystems. It can outcompete native species and diminish water quality,’ experts warned in a social media statement on 24 February 2025.
This follows previous detections along the Brisbane River, where the clam was first discovered in early 2024.
Despite its small size – typically less than 25mm, but capable of growing up to 65mm – the freshwater gold clam is a huge threat to Australia’s freshwater ecosystems.
Experts warn that this pest has an alarming ability to multiply, thanks to its rapid growth, short lifespan, and high reproductive rate.
It spreads easily through water currents, ballast water, and even the aquarium trade.

The freshwater gold clam – a species first recorded in Australia in February 2024 – has now been detected in multiple locations across Brisbane’s river systems
Once established, it can outcompete native species, clog pipes and pumps, and degrade water quality – causing serious environmental and economic consequences.
The freshwater gold clam is already well-established in New Zealand, North America, and South America, but its arrival in Australia has left authorities scrambling to contain it.
The federal agriculture and fisheries department revealed that the National Biosecurity Management Consultative Committee convened in January 2024 and decided that eradicating the clam from Queensland was not possible.
This decision was made based on the assessment that the species is now firmly established in the Ipswich region of the Brisbane River and that no effective eradication methods currently exist.
‘Freshwater gold clam has not been successfully eradicated from any locality it has invaded globally,’ the department said.
Biosecurity Queensland believes the pest was most likely transported via ballast water from ships or accidentally introduced through the aquarium trade.
While some invasive species can be spread by migratory birds, experts say this is unlikely in this case, as the clam requires water to transfer successfully.
Authorities are urging people to stay vigilant when near Queensland’s waterways.

Despite its small size – typically less than 25mm, but capable of growing up to 65mm – the freshwater gold clam is a huge threat to Australia’s freshwater ecosystems
If you spot what you believe to be a freshwater gold clam, you should report it immediately to Biosecurity Queensland.
Additionally, to help prevent further spread, Queenslanders are being advised to check, clean, and dry any boats or equipment used in affected areas before moving to another waterway.
However, not all small clams are invasive.
The Corbicula australis, or ‘Little Basket Clam,’ is a native species that many may mistake for the freshwater gold clam.
Surveys at Lake Samsonvale in late 2024 confirmed healthy numbers of native clams, but no signs of the invasive species – a rare piece of good news in the ongoing battle against freshwater pests.
For now, the full extent of the freshwater gold clam’s spread remains unknown, but one thing is clear: early detection is key.
If left unchecked, this small invader could cause big problems for Australia’s waterways.