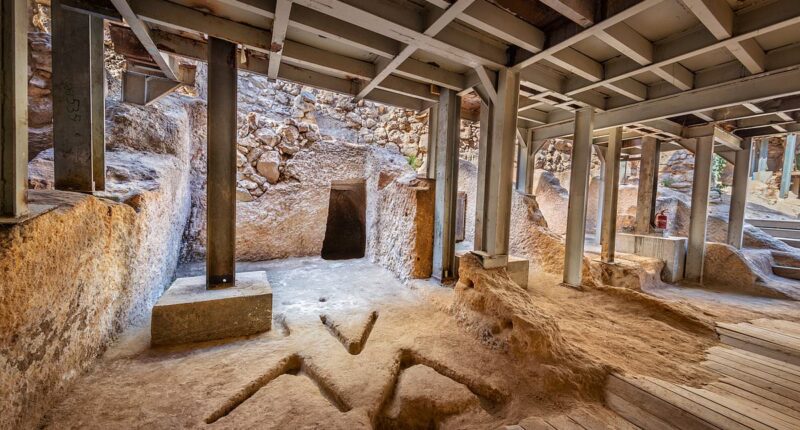
A place of worship sealed up by the ancestors of Jesus has been discovered in the ancient heart of Jerusalem, frozen in time for nearly 3,000 years.
Located near Temple Mount, the structure consists of eight rooms with various elements such as an altar, a sacred standing stone, and equipment for producing olive oil and wine.
It is believed by experts that the destruction of this structure may have been mentioned in the Bible, where Hezekiah, who is among Jesus’ ancestors, destroyed places of worship associated with idolatry.
This was one such place, according to Eli Shukron, exacavation director for the Israel Antiquities Authority (IAA), who dated it to Hezekiah’s reign.
He said: ‘The structure ceased to function during the 8th century BC, possibly as part of king Hezekiah’s religious reform.
‘According to the Bible, Hezekiah sought to centralise worship at the temple in Jerusalem, abolishing the ritual sites scattered across the kingdom.
‘The Bible describes how, during the First Temple period, additional ritual sites operated outside the temple.
‘It says two kings of Judah – Hezekiah and Josiah – implemented reforms to eliminate these sites and concentrate worship at the temple.’
Both kings are identified as paternal grandfathers of Jesus by the Gospel of Matthew.
Hezekiah’s crackdown against pagan places of worship – or ‘high places’ – is described in the second book of Kings.
It recounts how he ‘removed the high places, smashed the sacred stones’ and ‘did what was right in the eyes of the lord’.
Remarkably, the sacred standing stone at the site survived his onslaught.
Shukron called it ‘the most dramatic and important find in the excavation’.
‘This is what makes this place a cultic site,’ he said.
‘When we uncovered it, we found it standing in its place, with stones around it.
‘The standing stone was covered with earth; it was preserved – no one destroyed it.
‘When we found it, it was exactly as it was here 2,800 years ago.’
Another room featured the remains of an altar, identifiable by a drainage channel which still ran from its corner.
And in one part of the site, mysterious v-shaped carvings marked the floor.
Their true purpose is lost to history, but they might once have supported some sort of tripod with ritual use.
Archaeologists also found a hoard of artifacts from the 8th century BC, sealed behind a stone wall in a cave.
Among the artifacts found at the site are cooking pots, jars with fragments of ancient Hebrew inscriptions, loom weights, scarabs, stamped seals featuring decorative designs, and grinding stones used for crushing grains.
The site lies in the ancient heart of Jerusalem – sometimes called the City of David – just a few hundred metres from Temple Mount, and once co-existed with the First Temple there.
Excavations began in 2010, but the northern part of the ruins was discovered in 1909 by Montague Parker, a British adventurer searching for the Ark of the Covenant and other temple treasures.
Amichai Eliyahu, Israel’s Minister of Heritage, said: ‘This unique structure uncovered in the City of David is an exciting testimony to Jerusalem’s rich past.
‘Such discoveries make our connection and historic roots – going back thousands of years – tangible, in Jerusalem and other sites where the Jewish culture and belief system emerged.’
Shukron published his findings in ‘Atiqot, the IAA’s in-house journal.